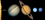






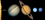






|
| Introduction |
|---|
Pluto was discovered on February 18, 1930, making it the last planet found in our Solar System. Pluto is usually farther from the Sun than any of the nine planets; however, due to the eccentricity of its orbit, it is closer than Neptune for 20 years out of its 249-year orbit. Pluto made its closest approach during 1989 and will remain within the orbit of Neptune until March 14, 1999.
Pluto's orbit is also highly inclined -- tilted 17 degrees to the orbital plane of the other planets. Observations also show that Pluto's spin axis is tipped by 122 degrees. Ground-based observations indicate that Pluto's surface is covered with methane ice and that there is a thin atmosphere that might freeze and fall to the surface as the planet moves away from the Sun. NASA plans to launch a spacecraft, the Pluto Express, in 2001 that will allow scientists to study the planet before its atmosphere freezes.
Pluto has one satellite named Charon [SHAR-on], named after the boatman in Greek mythology who operated the ferry across the River Styx to Pluto's realm in the underworld. Charon was discovered in 1978. Its surface composition seems to be different from Pluto's. The moon appears to be covered with water-ice rather than methane ice. Its orbit is gravitationally locked with Pluto, so both bodies always keep the same hemisphere facing each other. Pluto's and Charon's rotational periods and Charon's orbital period are
Pluto Statistics
Discovered by Clyde W. Tombaugh
Date of discovery February 18, 1930
Mass (kg) 1.29e+22
Mass (Earth = 1) 2.1586e-03
Equatorial radius (km) 1,160
Equatorial radius (Earth = 1) 1.8188e-01
Mean density (gm/cm^3) 2.05
Mean distance from the Sun (km) 5,913,520,000
Mean distance from the Sun (Earth = 1)) 39.5294
Rotational period (days) -6.3872
Orbital period (years) 248.54
Mean orbital velocity (km/sec) 4.74
Orbital eccentricity 0.2482
Tilt of axis (degrees) 122.52
Orbital inclination (degrees) 17.148
Equatorial surface gravity (m/sec^2) 0.4
Equatorial escape velocity (km/sec) 1.22
Visual geometric albedo 0.3
Magnitude (Vo) 15.12
Atmospheric composition 0.3
| Animations of Pluto and Charon |
|---|
| Views of Pluto & Charon |
|---|
 Pluto & Charon
Pluto & Charon
This view of Pluto was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. It shows a
rare image of tiny Pluto with its moon Charon, which is slightly
smaller than the planet. Because Pluto has not yet been visited by any
spacecraft, it remains a mysterious planet. Due to its great distance
from the sun, Pluto's surface is believed to reach temperatures as low
as -240°C (-400°F). From Pluto's surface, the Sun appears as
only a very bright star.
(Courtesy NASA)
 Hubble Telescope Image
Hubble Telescope Image
This is the clearest view yet of the distant planet Pluto and its moon,
Charon, as revealed by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The image was
taken on February 21, 1994, when the planet was 4.4 billion kilometers
(2.7 billion miles) from the Earth.
The HST corrected optics show the two objects as clearly separate and sharp disks. This now allows astronomers to measure directly (to within about 1 percent) Pluto's diameter of 2,320 kilometers (1,440 miles) and Charon's diameter of 1,270 kilometers (790 miles).
The HST observations show that Charon is bluer than Pluto. This means
that the worlds have different surface composition and structure. A
bright highlight on Pluto indicates that it might have a smoothly
reflecting surface layer. A detailed analysis of the HST image also
suggests that there is a bright area parallel to the equator of Pluto.
However, subsequent observations are needed to confirm that this feature
is real. The new HST image was taken when Charon was near its maximum
elongation from Pluto (0.9 arcseconds). The two worlds are 19,640
kilometers (12,200 miles) apart.
(Courtesy NASA/ESA/ESO)
 The Surface of Pluto
The Surface of Pluto
The never-before-seen surface of the distant planet Pluto is resolved
in these NASA Hubble Space Telescope pictures. These images,
which were made in blue light, show that Pluto is an unusually complex
object, with more large-scale contrast than any planet, except Earth.
Pluto probably shows even more contrast and perhaps sharper
boundaries between light and dark areas than is shown here, but
Hubble's resolution (just like early telescopic views of Mars) tends to
blur edges and blend together small features sitting inside larger
ones.
The two smaller inset pictures at the top are actual images from
Hubble. North is up. Each square pixel (picture element) is more than
100 miles across. At this resolution, Hubble discerns roughly 12 major
"regions" where the surface is either bright or dark.
The larger images (bottom) are from a global map constructed through
computer image processing performed on the Hubble data.
Opposite hemispheres of Pluto are seen in these two views.
(Courtesy NASA/ESA/ESO)
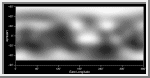 Map of the Surface of Pluto
Map of the Surface of Pluto
This is the first image-based surface map of the solar system's most
remote planet, Pluto.
The map, which covers 85% of the planet's surface, confirms that Pluto
has a dark equatorial belt and bright polar caps, as inferred from
ground-based light curves obtained during the mutual eclipses that
occurred between Pluto and its satellite Charon in the late 1980s.
The brightness variations in this map may be due to topographic features such as basins and fresh impact craters. However, most of the surface features are likely produced by the complex distribution of frosts that migrate across Pluto's surface with its orbital and seasonal cycles and chemical byproducts deposited out of Pluto's nitrogen-methane atmosphere. Names may later be proposed for some of the larger regions.
Image reconstruction techniques smooth out the coarse pixels in the
four raw images to reveal major regions where the surface is either
bright or dark. The black strip across the bottom corresponds to the
region surrounding Pluto's south pole, which was pointed away from
Earth when the observations were made, and could not be imaged.
(Courtesy NASA/ESA/ESO)
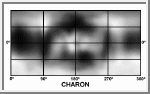 Map of the Surface of Charon
Map of the Surface of Charon
This is the first surface map of Charon, the moon of the solar
system's most remote planet, Pluto. The map is based on
photometric measurements. It covers the entire surface of the moon.
(Courtesy A.Tayfun Oner, based on pictures courtesy of Marc Buie/Lowell
Observatory)
 Ground vs. Hubble Comparison
Ground vs. Hubble Comparison
This image shows a comparison between a ground based view (left) and a
Hubble Space Telescope view (right) of Pluto and Charon.
 Nordic Optical Telescope
Nordic Optical Telescope
This image of Pluto was taken with the 2.6 meter
Nordic Optical
Telescope, located at La Palma, Canary Islands. It is a good
example of the best imagery that can be obtained from Earth-based
telescopes.
(© Copyright Nordic Optical Telescope Scientific Association -- NOTSA)
 Pluto Express
Pluto Express
This is a painting by Pat Rawlings of the Pluto Express mission scheduled
for launch in 2001 to arrive at Pluto around 2006-2008. The mission will
consist of a pair of small, fast, relatively cheap spacecraft weighing
less than 100 kilograms (220 pounds) each. The spacecraft will pass
within 15,000 kilometers (9,300 miles) of Pluto and Charon.
(Courtesy Pat Rawlings/NASA/JPL)

 Return to Neptune
Return to Neptune
 Visit
the Asteroids
Visit
the Asteroids